Mirtazapine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Originally branded Remeron, many generics |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697009 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% |
| Protein binding | 85% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP1A2, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4) |
| Biological half-life | 20–40 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (75%) Faeces (15%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | 6-Azamianserin, Org 3770 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.169.128 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
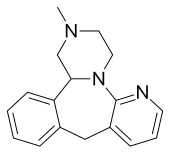
| Formula | C17H19N3 |
| Molar mass | 265.35 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| Density | 1.22 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 114 to 116 °C (237 to 241 °F) |
| Boiling point | 432 °C (810 °F) |
| Solubility in water | Soluble in methanol and chloroform mg/mL (20 °C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mirtazapine (originally branded Remeron, many generics) is an atypical antidepressant with noradrenergic and specific serotonergic activity. It blocks the α2 adrenergic auto- and heteroreceptors (enhancing norepinephrine release), and selectively antagonizes the 5-HT2 serotonin receptors in the central and peripheral nervous system. It also enhances serotonin neurotransmission at the 5-HT1 receptor and blocks the histaminergic (H1) and muscarinic receptors. Mirtazapine is not a serotonin or norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor but may increase serotonin and norepinephrine by other mechanisms of action.
Mirtazapine is a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (NaSSA) introduced by Organon International in the United States in 1996, and is used primarily in the treatment of depression. It is also commonly used as an anxiolytic, hypnotic, antiemetic and appetite stimulant. In structure, mirtazapine can also be classified as a tetracyclic antidepressant (TeCA) and is the 6-aza analogue of mianserin. It is also racemic – occurs as a combination of both (R)-(−)- and (S)-(+)-stereoisomers, both of which are active.
...
Wikipedia
