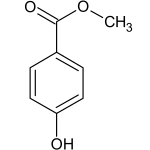
Methylparaben
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
|
|||
| Other names
Methyl paraben;
Methyl p-hydroxybenzoate; Methyl parahydroxybenzoate; Nipagin M; E number E218; Tegosept; Mycocten |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
99-76-3 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:31835 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL325372 |
||
| ChemSpider |
7176 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.532 | ||
| E number | E218 (preservatives) | ||
| 6273 | |||
| KEGG |
D01400 |
||
| PubChem | 7456 | ||
| UNII |
A2I8C7HI9T |
||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 152.15 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless crystals or white crystalline powder | ||
| UV-vis (λmax) | 255 nm (methanol) | ||
| -88.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related Parabens
|
Ethylparaben Propylparaben Butylparaben |
||
|
Related compounds
|
Methyl salicylate (ortho isomer) | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Methylparaben, also methyl paraben, one of the parabens, is a preservative with the chemical formula CH3(C6H4(OH)COO). It is the methyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Methylparaben serves as a pheromone for a variety of insects and is a component of queen mandibular pheromone. Some plants produce methylparaben, example thale cress. It is commonly used in the preparation of liquid dosage forms.
Methylparaben is an anti-fungal agent often used in a variety of cosmetics and personal-care products. It is also used as a food preservative and has the E number E218.
Methylparaben is commonly used as a fungicide in Drosophila food media. To Drosophila, methylparaben is toxic at higher concentrations, has an estrogenic effect, and slows the growth rate in the larval and pupal stages at lower concentrations.
There is controversy about whether methylparaben or propylparabens are harmful at concentrations typically used in body care or cosmetics. Methylparaben and propylparaben are considered generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for food and cosmetic antibacterial preservation. Methylparaben is readily metabolized by common soil bacteria, making it completely biodegradable.
Methylparaben is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract or through the skin. It is hydrolyzed to p-hydroxybenzoic acid and rapidly excreted in urine without accumulating in the body. Acute toxicity studies have shown that methylparaben is practically non-toxic by both oral and parenteral administration in animals. In a population with normal skin, methylparaben is practically non-irritating and non-sensitizing; however, allergic reactions to ingested parabens have been reported.
...
Wikipedia