Malonic acid
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Propanedioic acid
|
|
| Other names
Malonic acid
Methanedicarboxylic acid |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.003 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C3H4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 104.06 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.619 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 135 to 137 °C (275 to 279 °F; 408 to 410 K) (decomposes) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| Miscible | |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa1 = 2.83 pKa2 = 5.69 |
| -46.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions
|
malonate |
|
Related carboxylic acids
|
acetic acid oxalic acid propionic acid tartronic acid acrylic acid butyric acid succinic acid fumaric acid |
|
Related compounds
|
propanone propionaldehyde propanedial dimethyl malonate |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
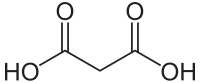
Malonic acid (IUPAC systematic name: propanedioic acid) is a dicarboxylic acid with structure CH2(COOH)2. The ionized form of malonic acid, as well as its esters and salts, are known as malonates. For example, diethyl malonate is malonic acid's diethyl ester. The name originates from the Greek word μᾶλον (malon) meaning 'apple'.
Malonic acid is often mistakenly believed to occur in beetroot at high concentration, and a study on the composition of sugar beet liquors revealed no malonic acid. It exists in its normal state as white crystals. Malonic acid is the classic example of a competitive inhibitor: It acts against succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) in the respiratory electron transport chain.
A classical preparation of malonic acid starts from chloroacetic acid:
Sodium carbonate generates the sodium salt, which is then reacted with sodium cyanide to provide the cyano acetic acid salt via a nucleophilic substitution. The nitrile group can be hydrolyzed with sodium hydroxide to sodium malonate, and acidification affords malonic acid. Industrially, however, malonic acid is produced by hydrolysis of dimethyl malonate or diethyl malonate.
...
Wikipedia
