Lindane
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682651 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Topical |
| ATC code | P03AB02 (WHO) QP53AB02 (WHO) QS02QA01 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 91% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic cytochrome P-450 oxygenase system |
| Biological half-life | 18 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
58-89-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 727 |
| DrugBank |
DB00431 |
| ChemSpider |
10481896 |
| UNII |
59NEE7PCAB |
| KEGG |
C07075 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:32888 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL15891 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.365 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
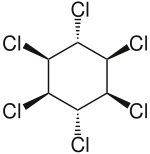
| Formula | C6H6Cl6 |
| Molar mass | 290.83 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Lindane, also known as gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane, (γ-HCCH), gammaxene, Gammallin and sometimes incorrectly called (BHC), is an organochlorine chemical variant of hexachlorocyclohexane that has been used both as an agricultural insecticide and as a pharmaceutical treatment for lice and scabies.
Lindane is a neurotoxin that interferes with GABA neurotransmitter function by interacting with the GABAA receptor-chloride channel complex at the picrotoxin binding site. In humans, lindane affects the nervous system, liver and kidneys, and may well be a carcinogen. It is unclear whether lindane is an endocrine disruptor.
The World Health Organization classifies lindane as "Moderately Hazardous," and its international trade is restricted and regulated under the Rotterdam Convention on Prior Informed Consent. In 2009, the production and agricultural use of lindane was banned under the on persistent organic pollutants. A specific exemption to that ban allows it to continue to be used as a second-line pharmaceutical treatment for lice and scabies.
The chemical was originally synthesised in 1825 by Faraday. It is named after the Dutch chemist Teunis van der Linden (1884–1965), the first to isolate and describe γ-Hexachlorcyclohexane in 1912. Its pesticidal action was discovered only in 1942, after which lindane production, by Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd (ICI), and use started up in the United Kingdom. It has been used to treat food crops and to forestry products, as a seed treatment, a soil treatment, and to treat livestock and pets. It has also been used as pharmaceutical treatment for lice and scabies, formulated as a shampoo or lotion. It is estimated that between 1950 and 2000, around 600,000 tonnes of lindane were produced globally, and the vast majority of which was used in agriculture. It has been manufactured by several countries, including the United States, China, Brazil, and several European countries, but as of 2007 only India and possibly Russia are still producing it.
...
Wikipedia
