Ginger
| Ginger | |
|---|---|
 |
|
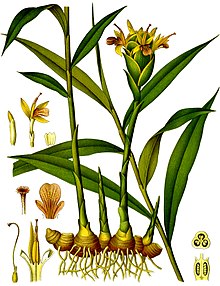
| 1896 color plate from Köhler's Medicinal Plants |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Zingiberales |
| Family: | Zingiberaceae |
| Genus: | Zingiber |
| Species: | Z. officinale |
| Binomial name | |
|
Zingiber officinale Roscoe 1807 |
|

A packet of ginger powder
|
|
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 1,404 kJ (336 kcal) |
|
71.62 g
|
|
| Sugars | 3.39 g |
| Dietary fiber | 14.1 g |
|
4.24 g
|
|
|
8.98 g
|
|
| Vitamins | |
| Thiamine (B1) |
(4%)
0.046 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(14%)
0.17 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(64%)
9.62 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
(10%)
0.477 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
(48%)
0.626 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
(3%)
13 μg |
| Vitamin C |
(1%)
0.7 mg |
| Vitamin E |
(0%)
0.0 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium |
(11%)
114 mg |
| Iron |
(152%)
19.8 mg |
| Magnesium |
(60%)
214 mg |
| Manganese |
(1586%)
33.3 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(24%)
168 mg |
| Potassium |
(28%)
1320 mg |
| Sodium |
(2%)
27 mg |
| Zinc |
(38%)
3.64 mg |
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database |
|

Ginger section
|
|
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 333 kJ (80 kcal) |
|
17.77 g
|
|
| Sugars | 1.7 g |
| Dietary fiber | 2 g |
|
0.75 g
|
|
|
1.82 g
|
|
| Vitamins | |
| Thiamine (B1) |
(2%)
0.025 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(3%)
0.034 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(5%)
0.75 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
(4%)
0.203 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
(12%)
0.16 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
(3%)
11 μg |
| Vitamin C |
(6%)
5 mg |
| Vitamin E |
(2%)
0.26 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium |
(2%)
16 mg |
| Iron |
(5%)
0.6 mg |
| Magnesium |
(12%)
43 mg |
| Manganese |
(11%)
0.229 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(5%)
34 mg |
| Potassium |
(9%)
415 mg |
| Sodium |
(1%)
13 mg |
| Zinc |
(4%)
0.34 mg |
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database |
|
Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a flowering plant whose rhizome, ginger root or simply ginger, is widely used as a spice or a folk medicine.
It is a herbaceous perennial which grows annual stems about a meter tall bearing narrow green leaves and yellow flowers. Ginger is in the family Zingiberaceae, to which also belong turmeric (Curcuma longa), cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum), and galangal. Ginger originated in the tropical rainforest in Southern Asia. Although ginger no longer grows wild, it is thought to have originated on the Indian subcontinent because the ginger plants grown in India show the largest amount of genetic variation. Ginger was exported to Europe via India in the first century AD as a result of the lucrative spice trade and was used extensively by the Romans.
The distantly related dicots in the genus Asarum are commonly called wild ginger because of their similar taste.
The origin of "ginger" is from the mid-14th century, from Old English gingifer, from Medieval Latin gingiber, from Latin zingiberi, from Greek zingiberis, from Prakrit (Middle Indic) singabera, from Sanskrit srngaveram, from srngam "horn" + vera- "body", from the shape of its root. But this may be Sanskrit folk etymology, and the word may be from an ancient Dravidian name that also produced the Tamil and Malayalam name for the spice, inchi-ver, from inchi "root." cf. gin (v.). The word probably was readopted in Middle English from Old French gingibre (modern French gingembre).
...
Wikipedia
