Zingiber
| Zingiber | |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
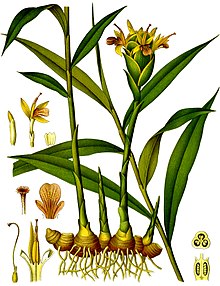
Zingiber officinale 1896 illustration |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Monocots |
| (unranked): | Commelinids |
| Order: | Zingiberales |
| Family: | Zingiberaceae |
| Genus: |
Zingiber Mill., 1754 |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The genus Zingiber is native to Southeast Asia, China, the Indian Subcontinent, and New Guinea. It contains the true gingers, plants grown the world over for their medicinal and culinary value. The most well-known is Z. officinale, garden ginger.
Each ginger species has a different culinary usage; for example, myoga is valued for the stem and flowers. Garden ginger's rhizome is the classic spice "ginger", and may be used whole, candied (known commonly as crystallized ginger), or dried and powdered. Other popular gingers used in cooking include cardamom and turmeric, though neither of these examples is a "true ginger" - they belong to different genera in the Zingiberaceae family.
The Plant List records the following accepted names for Zingiber species:
...
Wikipedia
