Geography of Djibouti
|
|
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Region | Horn of Africa |
| Area | Ranked 150th |
| • Total | 23,200 km2 (9,000 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 314 km (195 mi) |
| Borders | 510 km |
| Highest point |
Mousa Ali Volcano 2,028 m |
| Lowest point | Lac Assal, −155 m |
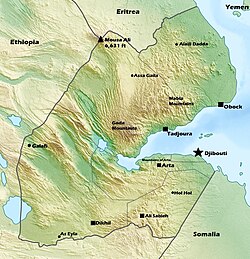
Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. To the east is its coastline on the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. Rainfall is sparse, and most of the territory has a semi-arid or arid environment. Lake Assal is a saline lake which lies 155 m (509 ft) below sea level, making it the lowest point on land in Africa and the third-lowest point on Earth after the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea. Djibouti's major settlements include the capital Djibouti City, the port towns of Tadjoura and Obock, and the southern cities of Ali Sabieh and Dikhil. It is the 151st largest country in the world by land area, covering a total of 23,200 km2, of which 23,180 km2 is land and 20 km2 is water.
Djibouti shares 127 kilometres (79 mi) of border with Eritrea, 344 kilometres (214 mi) with Ethiopia, and 63 kilometres (39 mi) with Somalia (total 530 km or 330 mi). It has a strategic location on the Horn of Africa and the Bab el Mandeb, along a route through the Red Sea and Suez Canal. Djibouti's coastline serves as a commercial gateway between the Arabian Peninsula and the Horn region's interior. The country is also the terminus of rail traffic into Ethiopia.
Djibouti can be divided into four physiographic regions
...
Wikipedia
