GLUT-4
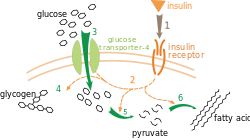
Glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT-4), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 4, is a protein encoded, in humans, by the SLC2A4 gene. GLUT4 is the insulin-regulated glucose transporter found primarily in adipose tissues and striated muscle (skeletal and cardiac). The first evidence for this distinct glucose transport protein was provided by David James in 1988. The gene that encodes GLUT4 was cloned and mapped in 1989.
At the cell surface, GLUT4 permits the facilitated diffusion of circulating glucose down its concentration gradient into muscle and fat cells. Once within cells, glucose is rapidly phosphorylated by glucokinase in the liver and hexokinase in other tissues to form glucose-6-phosphate, which then enters glycolysis or is polymerized into glycogen. Glucose-6-phosphate cannot diffuse back out of cells, which also serves to maintain the concentration gradient for glucose to passively enter cells.
...
Wikipedia