Hexokinase
| Hexokinase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Crystal structures of hexokinase 1 from Kluyveromyces lactis.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.7.1.1 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9001-51-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
| hexokinase 1 | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | HK1 |
| Entrez | 3098 |
| HUGO | 4922 |
| OMIM | 142600 |
| RefSeq | NM_000188 |
| UniProt | P19367 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 10 q22 |
| hexokinase 2 | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | HK2 |
| Entrez | 3099 |
| HUGO | 4923 |
| OMIM | 601125 |
| RefSeq | NM_000189 |
| UniProt | P52789 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 2 p13 |
| hexokinase 3 (white cell) | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | HK3 |
| Entrez | 3101 |
| HUGO | 4925 |
| OMIM | 142570 |
| RefSeq | NM_002115 |
| UniProt | P52790 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 5 q35.2 |
| Hexokinase_1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

crystal structure of human glucokinase
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Hexokinase_1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00349 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0108 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022672 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00370 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1cza | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1cza | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| Hexokinase_2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

rat brain hexokinase type i complex with glucose and inhibitor glucose-6-phosphate
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Hexokinase_2 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF03727 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0108 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022673 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00370 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1cza | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1cza | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
A hexokinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate of hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important product. Hexokinase can transfer an inorganic phosphate group from ATP to a substrate.
Hexokinases should not be confused with glucokinase, which is a specific isoform of hexokinase. While other hexokinases are capable of phosphorylating several hexoses, glucokinase acts with a 50-fold lower substrate affinity and its only hexose substrate is glucose.
Genes that encode hexokinase have been discovered in every domain of life, and exist among a variety of species that range from bacteria, yeast, and plants to humans and other vertebrates. They are categorized as actin fold proteins, sharing a common ATP binding site core that is surrounded by more variable sequences which determine substrate affinities and other properties.
Several hexokinase isoforms or isozymes that provide different functions can occur in a single species.
The intracellular reactions mediated by hexokinases can be typified as:
where hexose-CH2OH represents any of several hexoses (like glucose) that contain an accessible -CH2OH moiety. 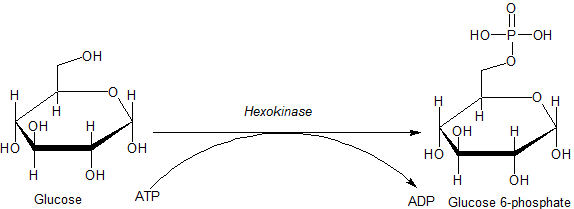
Phosphorylation of a hexose such as glucose often limits it to a number of intracellular metabolic processes, such as glycolysis or glycogen synthesis. This is because phosphorylated hexoses are charged, and thus more difficult to transport out of a cell.
...
Wikipedia
