Furans
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Furan
|
|||
|
Systematic IUPAC name
Oxole
5-Oxacyclopenta-1,3-diene 5-Oxacyclo-1,3-pentadiene 1,4-Epoxybuta-1,3-diene 1,4-Epoxy-1,3-butadiene |
|||
| Other names
Furfuran
Furane (misspelling) Divinylene oxide |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
110-00-9 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:35559 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL278980 |
||
| ChemSpider |
7738 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.390 | ||
| KEGG |
C14275 |
||
| PubChem | 8029 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4O | |||
| Molar mass | 68.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless, volatile liquid | ||
| Density | 0.936 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | −85.6 °C (−122.1 °F; 187.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 31.3 °C (88.3 °F; 304.4 K) | ||
| -43.09·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | Pennakem | ||
| R-phrases | R26/27/28, R45 | ||
| S-phrases | S16, S37, S45, S28 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | −69 °C (−92 °F; 204 K) | ||
| 390 °C (734 °F; 663 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | Lower: 2.3% Upper: 14.3% at 20 °C |
||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
> 2 g/kg (rat) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related heterocycles
|
Pyrrole Thiophene |
||
|
Related compounds
|
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) 2,5-Dimethylfuran Benzofuran Dibenzofuran |
||
| Structure | |||
| C2v | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
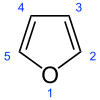
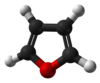
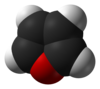
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen. The class of compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
Furan is a colorless, flammable, highly volatile liquid with a boiling point close to room temperature. It is soluble in common organic solvents, including alcohol, ether, and acetone, and is slightly soluble in water. It is toxic and may be carcinogenic in humans. Furan is used as a starting point to other specialty chemicals.
The name "furan" comes from the Latin furfur, which means bran. The first furan derivative to be described was 2-furoic acid, by Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1780. Another important derivative, furfural, was reported by Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner in 1831 and characterised nine years later by John Stenhouse. Furan itself was first prepared by Heinrich Limpricht in 1870, although he called it "tetraphenol" (as if it were a four-carbon analog to phenol, C6H6O).
Industrially, furan is manufactured by the palladium-catalyzed decarbonylation of furfural, or by the copper-catalyzed oxidation of 1,3-butadiene:
...
Wikipedia