Felodipine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Plendil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a692016 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 15% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Onset of action | 2.5–5 hours |
| Biological half-life | 25 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.305 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
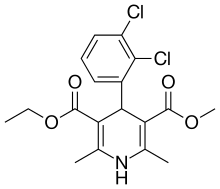
| Formula | C18H19Cl2NO4 |
| Molar mass | 384.259 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Felodipine is a medication of the calcium channel blocker type which is used to treat high blood pressure.
Felodipine is used to treat high blood pressure and stable angina.
It should not be used for people who are pregnant, have acute heart failure, are having a heart attack, have an obstructed heart valve, or have obstructions that block bloodflow out of the heart.
For people with liver failure the dose needs to be lowered, because felodipine is cleared by the liver.
Felodipine is metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4, so substances that inhibit or activate CYP3A4 can strongly effect how much felodipine is present.
CYP3A4 inhibitors, which increase the amount of felodipine available per dose, include cimetidine, erythromycin, itraconazole, , HIV protease inhibitors, and grapefruit juice.
CYP3A4 activators, which decrease the amount of felodipine available per dose, include phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampicin, barbiturates, efavirenz, nevirapine, and Saint John's wort.
The only very common side effect, occurring in more than 1/10 people, is edema in the arms and legs.
Common side effects, occurring in between 1% and 10% of people, include flushing, headache, heart palpitations, dizziness and fatigue.
...
Wikipedia
