English language learning and teaching
| English | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈɪŋɡlɪʃ/ |
| Region | Originally England now worldwide (see Geographical distribution, below) |
|
Native speakers
|
360–400 million (2006) L2 speakers: 400 million; as a foreign language: 600–700 million |
|
Early forms
|
|
|
Manually coded English (multiple systems) |
|
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | en |
| ISO 639-2 | |
| ISO 639-3 | |
| Glottolog | stan1293 |
| Linguasphere | 52-ABA |
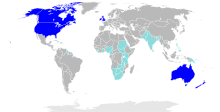
Countries of the world where English is a majority native language
Countries where English is official but not a majority native language
|
|
English is a West Germanic language that was first spoken in early medieval England and is now the global lingua franca. Named after the Angles, one of the Germanic tribes that migrated to England, it ultimately derives its name from the Anglia (Angeln) peninsula in the Baltic Sea. It is most closely related to the Frisian languages, although its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by other Germanic languages in the early medieval period, and later by Romance languages, particularly French. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in almost 60 sovereign states. It is the most commonly spoken language in the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Australia, Ireland, and New Zealand, and is widely spoken in some areas of the Caribbean, Africa, and South Asia. It is the third most common native language in the world, after Mandarin and Spanish. It is the most widely learned second language and an official language of the United Nations, of the European Union, and of many other world and regional international organisations. It is the most widely spoken Germanic language, accounting for at least 70% of speakers of this Indo-European branch.
English has developed over the course of more than 1,400 years. The earliest forms of English, a set of Anglo-Frisian dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the fifth century, are called Old English. Middle English began in the late 11th century with the Norman conquest of England, and was a period in which the language was influenced by French.Early Modern English began in the late 15th century with the introduction of the printing press to London and the King James Bible, and the start of the Great Vowel Shift. Through the worldwide influence of the British Empire, modern English spread around the world from the 17th to mid-20th centuries. Through all types of printed and electronic media, as well as the emergence of the United States as a global superpower, English has become the leading language of international discourse and the lingua franca in many regions and in professional contexts such as science, navigation, and law.
...
Wikipedia
