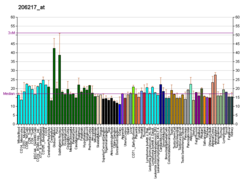
Ectodysplasin A
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
NP_001005609
NP_001005610
NP_001005612
NP_001005613
NP_001390
n/a
Ectodysplasin A (EDA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EDA gene.
Ectodysplasin A is a transmembrane protein of the TNF family which plays an important role in the development of ectodermal tissues such as skin in humans. It is recognized by the ectodysplasin A receptor.
The protein encoded by this gene is a type II membrane protein that can be cleaved by furin to produce a secreted form. The encoded protein, which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family, acts as a homotrimer and may be involved in cell-cell signaling during the development of ectodermal organs. Along with c-Met, it has been shown to be involved in the differentiation of anatomical placodes, precursors of scales, feathers and hair follicles in vertebrates. Defects in this gene are a cause of ectodermal dysplasia, anhidrotic, which is also known as X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Several transcript variants encoding many different isoforms have been found for this gene.
...
Wikipedia