Chromium trioxide
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Chromium trioxide
|
|
| Other names
Chromic anhydride, Chromium(VI) oxide, Chromic acid (misnomer)
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
1333-82-0 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:48240 |
| ChemSpider |
14212 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.189 |
| PubChem | 14915 |
| RTECS number | GB6650000 |
| UNII |
8LV49809UC |
| UN number | 1463 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| CrO3 | |
| Molar mass | 99.99 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Dark red granular solid, deliquescent |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 2.7 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 197 °C (387 °F; 470 K) |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) decomposes |
| 164.8 g/100 mL (0 °C) 169 g/100 mL (25 °C) 172.6 g/100 mL (40 °C) 198.1 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
|
| Solubility | Soluble in H2SO4, HNO3, (C2H5)2O, CH3COOH, acetone |
| +40·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Thermochemistry | |
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
73.2 J/mol·K |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−589.3 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 1194 |
| GHS pictograms |
    
|
| GHS signal word | Danger |
| H271, H301, H311, H314, H317, H330, H334, H340, H350, H361, H372, H410 | |
| P201, P220, P260, P273, P280, P284 | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
Carc. Cat. 1 Muta. Cat. 2 Repr. Cat. 3 |
| R-phrases | R45, R46, R9, R24/25, R26, R35, R42/43, R48/23, R50/53, R62 |
| S-phrases | S53, S45, S60, S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
80 mg/kg (rats, oral) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Chromium trioxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name. This compound is a dark-purple solid under anhydrous conditions, bright orange when wet and which dissolves in water concomitant with hydrolysis. Millions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly for electroplating. Chromium trioxide is a powerful oxidiser and a suspected carcinogen.
Chromium trioxide is generated by treating sodium chromate or the corresponding sodium dichromate with sulfuric acid:
Approximately 100M kg are produced annually by this or similar routes.
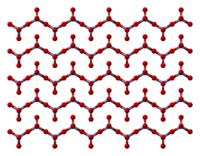
The solid consists of chains of tetrahedrally coordinated chromium atoms that share vertices. Each chromium center, therefore, shares two oxygen centers with neighbors. Two oxygen atoms are not shared, giving an overall stoichiometry of 1:3.
The structure of monomeric CrO3 has been calculated using density functional theory, and is predicted to be pyramidal (point group C3v) rather than planar (point group D3h).
Chromium trioxide decomposes above 197 °C liberating oxygen eventually giving Cr2O3:
It is used in organic synthesis as an oxidant, often as a solution in acetic acid, or acetone in the case of the Jones oxidation. In these oxidations, the Cr(VI) converts primary alcohols to the corresponding carboxylic acids and secondary alcohols to ketones. The reactions are given below:
...
Wikipedia

