Carmustine
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
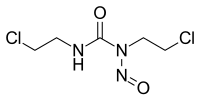
1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea
|
|
| Other names
N,N’-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-N-nitrosourea
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
154-93-8 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:3423 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL513 |
| ChemSpider |
2480 |
| DrugBank |
DB00262 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.309 |
| EC Number | 205-838-2 |
| KEGG |
D00254 |
| MeSH | Carmustine |
| PubChem | 2578 |
| RTECS number | YS2625000 |
| UNII |
U68WG3173Y |
| UN number | 2811 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C5H9Cl2N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 214.05 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Melting point | 30 °C (86 °F; 303 K) |
| log P | 1.375 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.194 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.803 |
| Pharmacology | |
| L01AD01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |
 
|
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| H300, H350, H360 | |
| P301+310, P308+313 | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| R-phrases | R45, R46, R60, R61, R28 |
| S-phrases | S22, S36/37/39, S45 |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
20 mg kg−1(oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related ureas
|
Dimethylurea |
|
Related compounds
|
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Carmustine (bis-chloroethylnitrosourea, BCNU, BiCNU) is a medication used mainly for chemotherapy and sometimes for immunosuppression before organ transplantation. It is a nitrogen mustard β-chloro-nitrosourea compound used as an alkylating agent. As a dialkylating agent, BCNU is able to form interstrand crosslinks in DNA, which prevents DNA replication and DNA transcription.
It has the appearance of an orange-yellow solid.
Carmustine for injection was earlier marketed under the name BiCNU by Bristol-Myers Squibb and now by Emcure Pharmaceuticals. In India it is sold under various brand names, including Consium.
It is used in the treatment of several types of brain cancer (including glioma, glioblastoma multiforme, medulloblastoma and astrocytoma), multiple myeloma and lymphoma (Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin). BCNU is sometimes used in conjunction with alkyl guanine transferase (AGT) inhibitors, such as O6-benzylguanine. The AGT-inhibitors increase the efficacy of BCNU by inhibiting the direct reversal pathway of DNA repair, which will prevent formation of the interstrand crosslink between the N1 of guanine and the N3 of cytosine.
...
Wikipedia
