Buformin
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.662 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
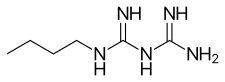
| Formula | C6H15N5 |
| Molar mass | 157.22 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Buformin (1-butylbiguanide) is an oral antidiabetic drug of the biguanide class, chemically related to metformin and phenformin. Buformin was marketed by German pharmaceutical company Grünenthal as Silubin.
Buformin hydrochloride is a fine, white to slightly yellow, crystalline, odorless powder, with a weakly acidic bitter taste. Its melting point is 174 to 177 °C, it is a strong base, and is freely soluble in water, methanol and ethanol, but insoluble in chloroform and ether. Toxicity: guinea pig LD50 subcutaneous 18 mg/kg; mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 140 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg oral. The partition coefficient (log P in octanol-water) is -1.20E+00; its water solubility is 7.46E+05 mg/l at 25 °C. Vapor pressure is 1.64E-04 mm Hg at 25 °C (EST); Henry's law constant is 8.14E-16 atm-m3/mole at 25 °C (EST). Its Atmospheric -OH rate constant is 1.60E-10 cm3/molecule-sec at 25 °C.
Buformin delays absorption of glucose from the gastrointestinal tract, increases insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake into cells, and inhibits synthesis of glucose by the liver. Buformin and the other biguanides are not hypoglycemic, but rather antihyperglycemic agents. They do not produce hypoglycemia; instead, they reduce basal and postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetics. Biguanides may antagonize the action of glucagon, thus reducing fasting glucose levels.
After oral administration of 50 mg of buformin to volunteers, almost 90% of the applied quantity was recovered in the urine; the rate constant of elimination was found to be 0.38 per hr. Buformin is a strong base (pKa = 11.3) and not absorbed in the stomach. After intravenous injection of about 1 mg/kg buformin-14-C, the initial serum concentration is 0.2-0.4 µg/ml. Serum level and urinary elimination rate are linearly correlated. In man, after oral administration of 50 mg 14-C-buformin, the maximum serum concentration was 0.26-0.41 µg/ml. The buformin was eliminated with an average half-life of 2 h. About 84% of the dose administered was found excreted unchanged in the urine. Buformin is not metabolized in humans. The bioavailability of oral buformin and other biguanides is 40%-60%. Binding to plasma proteins is absent or very low.
...
Wikipedia
