Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
| Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | non-Hodgkin disease |
 |
|
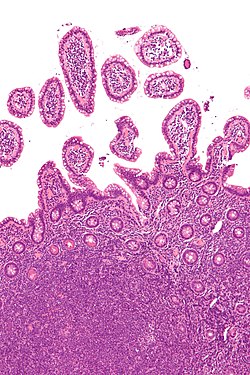
| Micrograph of mantle cell lymphoma, a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Terminal ileum. H&E stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | hematology and oncology |
| ICD-10 | C82-C85 |
| ICD-9-CM | 200, 202 |
| ICD-O | 9591/3 |
| OMIM | 605027 |
| DiseasesDB | 9065 |
| MedlinePlus | 000581 |
| eMedicine | med/1363 ped/1343 |
| Patient UK | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| MeSH | D008228 |
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphoma except Hodgkin's lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow growing while others are fast growing.
Lymphomas are types of cancer that develops from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. Risk factors include poor immune function, autoimmune diseases, Helicobacter pylori infection, hepatitis C, obesity, and Epstein-Barr virus infection. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies lymphomas into five major groups, including one for Hodgkin's lymphoma. Within the four groups for NHL there are over 60 specific types of lymphoma. Diagnosis is by examination of a bone marrow or lymph node biopsy. Medical imaging is done to help with cancer staging.
Treatment depends on if the lymphoma is slow or fast growing and if it is in one area or many areas. Treatments may include chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, stem cell transplantation, surgery, or watchful waiting. If the blood becomes overly thick due to antibodies, plasmapheresis may be used. Radiation and some chemotherapy, however, increase the risk of other cancers, heart disease or nerve problems over the subsequent decades.
...
Wikipedia
