Helicobacter pylori infection
| Helicobacter pylori | |
|---|---|
| Synonym | Campylobacter pylori |
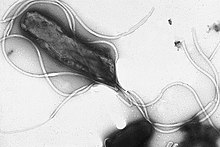
| staining of H. pylori from a gastric biopsy | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease, gastroenterology |
| Symptoms | None, abdominal pain, nausea |
| Causes | Helicobacter pylori spread by fecal oral route |
| Diagnostic method | Urea breath test, fecal antigen assay, tissue biopsy |
| Medication | Proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin, amoxicillin, metronidazole |
| Frequency | >50% |
| Helicobacter pylori | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Epsilonproteobacteria |
| Order: | Campylobacterales |
| Family: | Helicobacteraceae |
| Genus: | Helicobacter |
| Species: | H. pylori |
| Binomial name | |
|
Helicobacter pylori (Marshall et al. 1985) Goodwin et al., 1989 |
|
| Classification |
· ·
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
Helicobacter pylori, previously Campylobacter pylori, is a gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found usually in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Australian scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in a person with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions not previously believed to have a microbial cause. It is also linked to the development of duodenal ulcers and stomach cancer. However, over 80% of individuals infected with the bacterium are asymptomatic, and it may play an important role in the natural stomach ecology.
More than 50% of the world's population harbor H. pylori in their upper gastrointestinal tract. Infection is more common in developing countries than Western countries.H. pylori's helical shape (from which the genus name derives) is thought to have evolved to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach.
Up to 85% of people infected with H. pylori never experience symptoms or complications.Acute infection may appear as an acute gastritis with abdominal pain (stomach ache) or nausea. Where this develops into chronic gastritis, the symptoms, if present, are often those of non-ulcer dyspepsia: stomach pains, nausea, bloating, belching, and sometimes vomiting or black stool.
...
Wikipedia
