Butan-1-ol
|
|
|||
 |
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
Butan-1-ol
|
|||
| Other names
Butalcohol
Butanol |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | B00907 | ||
| 969148 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.683 | ||
| EC Number | 200-751-6 | ||
| 25753 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | 1-Butanol | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | EO1400000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1120 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C4H10O | |||
| Molar mass | 74.12 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless, refractive liquid | ||
| Odor | banana-like, harsh, alcoholic and sweet | ||
| Density | 0.81 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −89.8 °C (−129.6 °F; 183.3 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 117.7 °C (243.9 °F; 390.8 K) | ||
| 73 g L−1 at 25 °C | |||
| Solubility | very soluble in acetone miscible with ethanol, ethyl ether |
||
| log P | 0.839 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 6 mmHg (20 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 16.10 | ||
| -56.536·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3993 (20 °C) | ||
| Viscosity | 2.573 mPa×s (at 25 °C) | ||
| 1.66 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
225.7 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−328(4) kJ mol−1 | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH |
−2670(20) kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 0111 | ||
|
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
|||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R10, R22, R37/38, R41, R67 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S2), S7/9, S13, S26, S37/39, S46 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 35 °C (95 °F; 308 K) | ||
| 343 °C (649 °F; 616 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.45–11.25% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
790 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
|
LDLo (lowest published)
|
3484 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 790 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1700 mg/kg (dog, oral) |
||
|
LC50 (median concentration)
|
9221 ppm (mammal) 8000 ppm (rat, 4 hr) |
||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 100 ppm (300 mg/m3) | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
C 50 ppm (150 mg/m3) [skin] | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1400 ppm | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
Butanethiol n-Butylamine Diethyl ether Pentane |
||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Butanol
1-Butanol
Butyl alcohol
Butyl hydrate
Butylic alcohol
Butyralcohol
Butyric alcohol
Butyryl alcohol
n-Butyl alcohol
1-Hydroxybutane
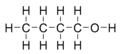
n-Butanol or n-butyl alcohol or normal butanol is a primary alcohol with a 4-carbon structure and the chemical formula C4H9OH. Its isomers include isobutanol, 2-butanol, and tert-butanol. Butanol is one of the group of "fusel alcohols" (from the German for "bad liquor"), which have more than two carbon atoms and have significant solubility in water.
n-Butanol occurs naturally as a minor product of the fermentation of sugars and other carbohydrates, and is present in many foods and beverages. It is also a permitted artificial flavorant in the United States, used in butter, cream, fruit, rum, whiskey, ice cream and ices, candy, baked goods and cordials. It is also used in a wide range of consumer products.
The largest use of n-butanol is as an industrial intermediate, particularly for the manufacture of butyl acetate (itself an artificial flavorant and industrial solvent). It is a petrochemical, manufactured from propylene and usually used close to the point of manufacture. Estimated production figures for 1997 are: United States 784,000 tonnes; Western Europe 575,000 tonnes; Japan 225,000 tonnes.
n-Butanol is produced industrially from the petrochemical feedstock propylene. Propylene is hydroformylated to butyraldehyde (oxo process) in the presence of a rhodium-based homogeneous catalyst similar to Wilkinson's catalyst. The butyraldehyde is then hydrogenated to produce n-butanol.
...
Wikipedia