Alytes obstetricans
| Common midwife toad | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Alytidae |
| Genus: | Alytes |
| Species: | A. obstetricans |
| Binomial name | |
|
Alytes obstetricans (Laurenti, 1768) |
|
 |
|
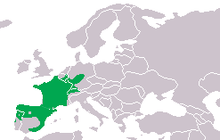
The common midwife toad (Alytes obstetricans) is a species of midwife frog in the family Alytidae (formerly Discoglossidae). It is found in Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom (although, in the latter, only as an introduction). Like other members of its genus (Alytes), the male toad carries the eggs around entwined on his back and thighs until they are ready to hatch.
Its natural habitats are temperate forests, dry forests, shrubland, rivers, freshwater lakes, freshwater marshes, temperate desert, arable land, pastureland and urban areas. It is threatened by habitat loss.
The common midwife toad can grow to a length of 5.5 centimetres (2.2 in) but is usually rather smaller than this, the females generally being larger than the males. It is broad and stocky and has a large head with prominent eyes, the pupils being vertical slits. The skin is mostly smooth with a few small warts and granules and a row of large warts down either side. The parotoid glands are small and there are additional glands in the under arm and ankle regions. There are three tubercles on each metacarpal. The colour is quite variable, often being grey, olive or brown, sometimes speckled with small greenish or brown spots. The large warts are often reddish or yellow. The underside is pale grey often with spots of darker grey on the throat and chest.
...
Wikipedia

