Woodhenge
|
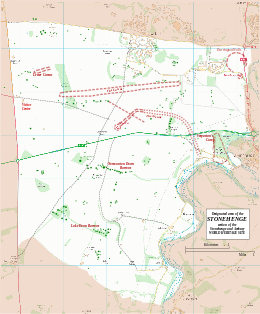
Map showing Woodhenge and Durrington Walls within the Stonehenge section of the Stonehenge and Avebury World Heritage Site
|
|
| Location | OS SU150434 |
|---|---|
| Region | Wiltshire |
| Coordinates | 51°11′22″N 1°47′09″W / 51.1894°N 1.78576°WCoordinates: 51°11′22″N 1°47′09″W / 51.1894°N 1.78576°W |
| Type | henge |
| History | |
| Periods | Neolithic |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1926-8 |
| Archaeologists | Ben and Maud Cunnington |
| Condition | feint earthworks, concrete posts |
| Public access | Yes |
| Website | English Heritage |
| Designated | 1986 |
| Reference no. | 373 |
| Designated | 1929 |
| Reference no. | 1009133 |
Woodhenge is a Neolithic Class II henge and timber circle monument located in the Stonehenge World Heritage Site in Wiltshire, England. It is 2 miles (3.2 km) north-east of Stonehenge in the parish of Durrington, just north of Amesbury.
Woodhenge was identified from an aerial photograph taken by Squadron Leader (later Group Captain) Gilbert Insall, VC, in 1926. during the same period that an aerial archaeology survey of Wessex by Alexander Keiller and OGS Crawford (Archaeology Officer for the Ordnance Survey) was also being undertaken. Although some sources attribute the identification of the henge to Crawford, Crawford himself credits its discovery to Gilbert Insall. However the site had been previously found in the early 19th century and described as an earthworks and thought to be a disc barrow. It was originally called Dough Cover. Maud Cunnington and B.H.Cunnington subsequently excavated the site between 1926 and 1929. confirming that it was indeed a henge.
Pottery from the excavation was identified as being consistent with the grooved ware style of the middle Neolithic, although later Beaker sherds were also found. So, the structure was probably built during the period of cultural similarities commonly known as the Beaker. The Beaker culture spans both the Late Neolithic and Britain's Early Bronze Age and includes both the distinctive "bell beaker" type ceramic vessels for which the cultural grouping is known as well as other local styles of pottery from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age.
...
Wikipedia