Visnagin
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
4-Methoxy-7-methyl-5H-furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-5-one
|
|
| Other names
Visnacorin; Khella; Desmethoxykhellin; 5-Methoxy-2-methylfuranochromone; 5-Methoxy-2-methyl-6,7-furanochrome
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 5-19-06-00030 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.301 |
| EC Number | 201-430-3 |
| 234955 | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | LV1420000 |
|
|
| Properties | |
| C13H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 230.22 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Melting point | 144 to 145 °C (291 to 293 °F; 417 to 418 K) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | ethanol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful by ingestion |
| Safety data sheet | [1] |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | WARNING |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
832 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Visnagin is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C13H10O4 It is a furanochromone, a compound derivative of chromone (1,4-benzopyrone) and furan.
Ammi visnaga, the main source for visnagin, has been used in traditional medicine in the Middle East to ease urinary tract pain associated with kidney stones and to promote stone passage.
Visnagin naturally occurs in Ammi visnaga, a species of flowering plant in the carrot family known by many common names, including bisnaga, toothpickweed, and khella. Visnagin-containing khella seeds are usually found mainly in Middle East countries such as Egypt and Turkey and also in Northern African countries such as Morocco. Visnagin can be extracted directly from khella seeds.
Modified synthesis of the naturally occurring visnagin is reported. Starting from phloroghrcin aldehyde, and building on the 2-methyl-y-pyrone, 2-methyl-5,7-dihydroxy-dfo-yl-chromone was obtained. Construction of the furan moiety was realized by a conventional method through the 7-carboxymethoxy ether giving S-norvisnagin which can be methylated to visnagin.
Visnagin analogs can be synthesized through the condensation of visnagone with esters and sodium. This leads to the product of 2-ethyl, 2-(3'-pyridyl) visnagin analog (50c).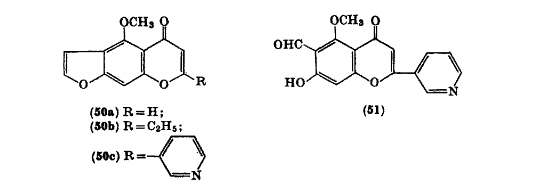
Visnagin molecules can go over an oligomerization to form a chain of visnagin molecules.
...
Wikipedia

