Venetian Republic
| Most Serene Republic of Venice | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
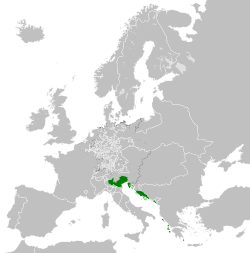
The Republic of Venice in 1789
|
||||||||||||||
| Capital |
Eraclea (697–742) Malamocco (742–810) Venice (810–1797) |
|||||||||||||
| Languages | Latin, Venetian, Italian | |||||||||||||
| Government | parliamentary merchant republic with elective monarchistic features. | |||||||||||||
| Doge | ||||||||||||||
| • | 697–717 (first) | Paolo Lucio Anafestoa | ||||||||||||
| • | 1789–1797 (last) | Ludovico Manin | ||||||||||||
| Legislature | Great Council | |||||||||||||
| • | Upper Chamber | Senate | ||||||||||||
| • | Lower Chamber | Council of Ten | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages - Early modern period | |||||||||||||
| • | Established1 | 697 | ||||||||||||
| • | Golden Bull of Alexios I |
1082 |
||||||||||||
| • | Fourth Crusade | 1202-04 | ||||||||||||
| • | Battle of Lepanto | 1571 | ||||||||||||
| • | Treaty of Leoben | 17 April 1797 | ||||||||||||
| • | Treaty Campo Formio | 18 October 1797 | ||||||||||||
| Currency |
Venetian ducat Venetian lira |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Today part of |
|
|||||||||||||
| a. ^ Paolo Lucio Anafesto is traditionally the first Doge of Venice, but John Julius Norwich suggests that this may be a mistake for Paul, Exarch of Ravenna, and that the traditional second doge Marcello Tegalliano may have been the similarly named magister militum to Paul. Their existence as doges is uncorroborated by any source before the 11th century, but as Norwich suggests, is probably not entirely legendary. Traditionally, the establishment of the Republic is, thus, dated to 697. | ||||||||||||||
The Republic of Venice (Italian: Repubblica di Venezia; Venetian: Repùblica Vèneta), traditionally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice (Italian: Serenissima Repubblica di Venezia; Venetian: Serenìsima Repùblica Vèneta), was a sovereign state and maritime republic in northeastern Italy, which existed for a millennium between the 8th century and the 18th century. It was based in the lagoon communities of the historically prosperous city of Venice. It was a leading European economic and trading power during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance.
The Venetian city state was founded as a safe haven for people escaping persecution in mainland Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire. In its early years, it prospered on the salt trade. In subsequent centuries, the city state established a thalassocracy. It dominated trade on the Mediterranean Sea, including commerce between Asia, Europe and North Africa. The Venetian navy was used in the Crusades. Venice achieved territorial conquests along the Adriatic Sea. The city became home to an extremely wealthy merchant class, who patronized renowned art and architecture along the city's lagoons. Venetian merchants were influential financiers in Europe. The city was also the birthplace of great European explorers, including Marco Polo, as well as the classical music composer Vivaldi.
...
Wikipedia