Vasculitis
| Vasculitis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
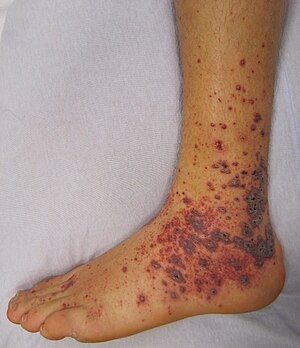
| Petechia and purpura on the lower limb due to medication-induced vasculitis. | |
| Pronunciation | /vaskjʊˈlʌɪtɪs/ |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology |
| ICD-10 | I77.6, I80, L95, M30-M31 |
| ICD-9-CM | 446, 447.6 |
| DiseasesDB | 13750 |
| Patient UK | Vasculitis |
| MeSH | D014657 |
Vasculitis (plural: vasculitides) is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily caused by leukocyte migration and resultant damage.
Although both occur in vasculitis, inflammation of veins (phlebitis) or arteries (arteritis) on their own are separate entities.
Possible symptoms include:
Vasculitis can be classified by the cause, the location, the type of vessel or the size of vessel.
According to the size of the vessel affected, vasculitis can be classified into:
Some disorders have vasculitis as their main feature. The major types are given in the table below:
Takayasu's arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa and giant cell arteritis mainly involve arteries and are thus sometimes classed specifically under arteritis.
Furthermore, there are many conditions that have vasculitis as an accompanying or atypical symptom, including:
In pediatric patients varicella inflammation may be followed by vasculitis of intracranial vessels. This condition is called post varicella angiopathy and this may be responsible for arterial ischaemic strokes in children.
Several of these vasculitides are associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. These are:
In this table: ANA = Antinuclear antibodies, CRP = C-reactive protein, ESR = Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, dsDNA = double-stranded DNA, ENA = extractable nuclear antigens, RNP = ribonucleoproteins; VDRL = Venereal Disease Research Laboratory
Treatments are generally directed toward stopping the inflammation and suppressing the immune system. Typically, corticosteroids such as prednisone are used. Additionally, other immune suppression drugs, such as cyclophosphamide and others, are considered. In case of an infection, antimicrobial agents including cephalexin may be prescribed. Affected organs (such as the heart or lungs) may require specific medical treatment intended to improve their function during the active phase of the disease.
...
Wikipedia
