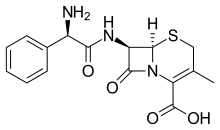
Cephalexin
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌsɛfəˈlɛksᵻn/ |
| Trade names | Keflex, Cepol, Ceporex, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682733 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth |
| ATC code | J01DB01 (WHO) QJ51DB01 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Well absorbed |
| Protein binding | 15% |
| Metabolism | 80% excreted unchanged in urine within 6 hours of administration |
| Biological half-life | For an adult with normal renal function, the serum half-life is 0.5–1.2 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
15686-71-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 2666 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 4832 |
| DrugBank |
DB00567 |
| ChemSpider |
25541 |
| UNII |
5SFF1W6677 |
| KEGG |
D00263 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:3534 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1727 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.142 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H17N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 347.39 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Melting point | 326.8 °C (620.2 °F) |
|
|
|
|
Cefalexin, also spelled cephalexin, is an antibiotic that can treat a number of bacterial infections. It kills gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria by disrupting the growth of the bacterial cell wall. Cefalexin is a beta-lactam antibiotic within the class of first-generation cephalosporins. It works similarly to other agents within this class, including intravenous cefazolin, but can be taken by mouth.
Cefalexin can treat certain bacterial infections, including those of the middle ear, bone and joint, skin, and urinary tract. It may also be used for certain types of pneumonia, , and to prevent bacterial endocarditis. Cefalexin is not effective against infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Enterococcus, or Pseudomonas. Like other antibiotics, cefalexin cannot treat viral infections, such as the flu, common cold or acute bronchitis. Cefalexin can be used in those who have mild or moderate allergies to penicillin. However, it is not recommended in those with severe penicillin allergies.
Common side effects include stomach upset and diarrhea. An allergic reaction and infection with Clostridium difficile, a type of diarrhea, is also possible. To date, no evidence of harm to the baby has been found when used during pregnancy or breast feeding. It can be used in children and those over 65 years of age. Those with kidney problems may require a decrease in dose.
...
Wikipedia
