Uveal melanoma
| Uveal melanoma | |
|---|---|
 |
|
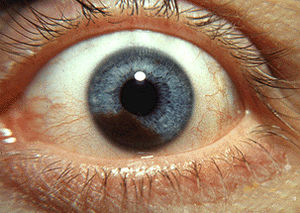
| Iris melanoma | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
| ICD-10 | C69 |
| ICD-9-CM | 190 |
| ICD-O | M8720/3 |
| OMIM | 155720 |
| DiseasesDB | 2614 |
| MedlinePlus | 001022 |
| eMedicine | oph/403 |
| MeSH | D014604 |
Uveal melanoma is a cancer (melanoma) of the eye involving the iris, ciliary body, or choroid (collectively referred to as the uvea). Tumors arise from the pigment cells (melanocytes) that reside within the uvea giving color to the eye. These melanocytes are distinct from the retinal pigment epithelium cells underlying the retina that do not form melanomas.
Uveal melanomas are the most common primary intraocular tumor in adults. The incidence has remained stable for several years.
The cause of uveal melanoma is unclear, but UV light is a risk factor. Uveal nevi are common (10% of caucasians), but rarely progress to melanoma.
Uveal melanomas, often referred to by the media and in the general population as ocular melanomas, may arise from any of the three parts of the uvea, and are sometimes referred to by their location, as choroidal melanoma, ciliary body melanoma, or iris melanoma. Large tumors often encompass multiple parts of the uvea and can be named accordingly. True iris melanomas, originating from within the iris as opposed to originating elsewhere and invading the iris, are distinct in their etiology and prognosis, such that the other tumors are often referred to collectively as Posterior uveal melanomas.
Uveal tumors can originate from melanocytes residing within the iris. Benign melanocytic tumors, such as iris freckles and moles (nevi), are common and pose no health risks, unless they show signs of malignancy, in which case they are classified as iris melanomas. Though derived from uveal melanocytes, iris melanomas share more in common with cutaneous (skin) melanomas, in that they frequently harbor BRAF mutations associated with ultraviolet damage. Iris melanomas are much less likely to metastasize than other uveal melanomas, and less likely to impair vision if detected and treated early. Approximately 5% of uveal melanomas involve the iris.
...
Wikipedia
