Tofacitinib
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xeljanz, Jakvinus |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Xeljanz |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 74% |
| Protein binding | 40% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (via CYP3A4 and CYP2C19) |
| Biological half-life | 3 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | CP-690550 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.215.928 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
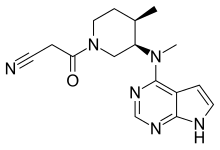
| Formula | C16H20N6O |
| Molar mass | 312.369 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Tofacitinib (INN) is a drug of the janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor class, discovered and developed by the National Institutes of Health and Pfizer. Tofacitinib is marketed as Xeljanz and Jakvinus.
It is currently approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in the United States and other countries.
It has demonstrated effectiveness in the treatment of psoriasis in Phase 3 studies. It is being studied for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease, and other immunological diseases, as well as for the prevention of organ transplant rejection.
In November 2012, the U.S. FDA approved tofacitinib "to treat adults with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to, or who are intolerant of, methotrexate." It was later approved in Japan, Switzerland and others (but not the EU). It is marketed as Xeljanz in all regions except for Russia where it will be marketed as Jakvinus or Jaquinus.
It is an inhibitor of the enzyme janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and janus kinase 3 (JAK 3), which means that it interferes with the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, which transmits extracellular information into the cell nucleus, influencing DNA transcription.
In a mouse model of established arthritis, tofacitinib rapidly improved disease by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators and suppressing STAT1-dependent genes in joint tissue. This efficacy in this disease model correlated with the inhibition of both JAK1 and 3 signaling pathways, suggesting that tofacitinib may exert therapeutic benefit via pathways that are not exclusive to inhibition of JAK3.
...
Wikipedia
