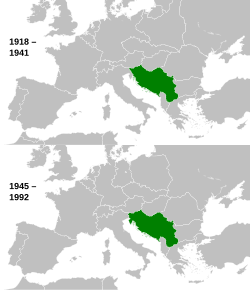
South Slavia
| Yugoslavia | |||||
| |||||
|
Anthem "Himna Kraljevine Jugoslavije" (1919–1941) "Hej, Slaveni" (1945–1992) | |||||
|
Yugoslavia during Interwar period and Cold War
| |||||
| Capital | Belgrade | ||||
| Government |
Kingdom of Yugoslavia (1918–1941) Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1945–1992) |
||||
| Historical era | 20th century | ||||
| • | Creation | 1 December 1918 | |||
| • | Axis invasion | 6 April 1941 | |||
| • | Abolition of monarchy | 29 November 1945 | |||
| • | Disintegration | 27 April 1992 | |||
| Currency | Yugoslav dinar | ||||
| Internet TLD | .yu | ||||
| Calling code | +38 | ||||
Yugoslavia (Serbo-Croatian: Jugoslavija/Југославија [juɡǒslaːʋija]; Slovene: Jugoslavija [juɡɔˈslàːʋija]; Macedonian: Југославија [juɡɔˈsɫavija]; Pannonian Rusyn: Югославия, transcr. Juhoslavija) was a country in Southeastern and Central Europe for most of the 20th century. It came into existence after World War I in 1918 under the name of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes by the merger of the provisional State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (itself formed from territories of the former Austro-Hungarian Empire) with the formerly independent Kingdom of Serbia. The Serbian royal House of Karađorđević became the Yugoslav royal dynasty. Yugoslavia gained international recognition on 13 July 1922 at the Conference of Ambassadors in Paris. The country was named after the South Slavic peoples and constituted their first union, following centuries in which the territories had been part of the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary.
...
Wikipedia