Sillaginopodys
| Club-foot whiting | |
|---|---|
 |
|
|
Not evaluated (IUCN 3.1)
|
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Perciformes |
| Family: | Sillaginidae |
| Genus: |
Sillaginopodys Fowler, 1933 |
| Species: | S. chondropus |
| Binomial name | |
|
Sillaginopodys chondropus Bleeker, 1849 |
|
 |
|
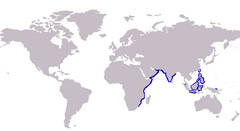
| Range of the club-foot whiting | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Sillago chondropus Bleeker, 1849 |
|
Sillago chondropus Bleeker, 1849
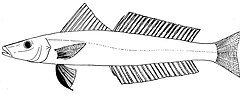
The club-foot whiting, Sillaginopodys chondropus, (also known as the Horrelvoet sillago), the only member of the genus Sillaginopodys, is a coastal marine fish of the smelt whiting family Sillaginidae that inhabits a wide range including west Africa, India and the northern Indonesian Archipelago. The species is unique in the morphology of the pelvic spine and fin, making identification of the species easier than most of its relatives. The species is of minor commercial importance, taken by seine net and marketed fresh throughout its range.
The club-foot whiting was first described and named by Pieter Bleeker in 1849, however the exact origin of the holotype specimen is unknown. Bleeker conducted most of his studies on the fishes of South East Asia, and one author has attributed the type specimen to samples collected from the Java Sea. The common name of the species, club-foot whiting, is derived from its unique pelvic fin structure which may look, and possibly act as club shaped 'foot'. The other common name; Horrelvoet sillago, is a name used in Africa and is derived from Afrikaans.
As with most of the family Sillaginidae, the club-foot whiting has a slightly compressed, elongate body tapering toward the terminal mouth, with the species reaching a maximum overall length of 35 cm. The body is covered in small ctenoid scales extending to the cheek and head, which has scales arranged in 3-4 rows. The first dorsal fin has 11 to 12 spines and the second dorsal fin has 1 leading spine with 20 to 22 soft rays posterior. The anal fin has 2 spines with 22 to 23 soft rays posterior to the spines. Possibly the most obvious identifying feature of the species is the characteristic pelvic fin, of which the first ray is modified into a laterally compressed club-like structure that overlaps the much reduced ventral spine at the base of the fin. Other distinguishing features include 66 to 73 lateral line scales and a total of 35 vertebrae.
...
Wikipedia
