Sertoli cells
| Sertoli cell | |
|---|---|
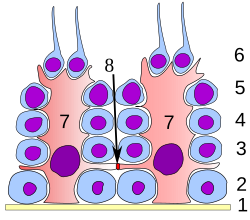
Germinal epithelium of the testicle.
1: basal lamina 2: spermatogonia 3: 1st order 4: spermatocyte 2nd order 5: spermatid 6: mature spermatid 7: Sertoli cell 8: tight junction (blood testis barrier) |
|

Histological section through testicular parenchyma of a boar.
1 Lumen of Tubulus seminiferus contortus 2 spermatids 3 4 spermatogonia 5 Sertoli cell 6 Myofibroblasts 7 Leydig cells 8 capillaries |
|
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | A05.360.444.849.789 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
A Sertoli cell (a kind of sustentacular cell) is a "nurse" cell of the testicles that is part of a seminiferous tubule and helps in the process of spermatogenesis; that is, the production of sperm.
It is activated by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secreted by the adenohypophysis, and has FSH receptor on its membranes. It is specifically located in the convoluted seminiferous tubules (since this is the only place in the testes where the spermatozoa are produced). Development of Sertoli cells is directed by the testis-determining factor protein.
Because its main function is to nourish the developing sperm cells through the stages of spermatogenesis, the Sertoli cell has also been called the "mother" or "nurse" cell. Sertoli cells also act as phagocytes, consuming the residual cytoplasm during spermatogenesis. Translocation of germ cells from the base to the lumen of the seminiferous tubules occurs by conformational changes in the lateral margins of the Sertoli cells.
Sertoli cells secrete the following substances:
The occluding junctions of Sertoli cells form the blood-testis barrier, a structure that partitions the interstitial blood compartment of the testis from the adluminal compartment of the seminiferous tubules. Because of the apical progression of the spermatogonia (sperm stem cells), the occluding junctions must be dynamically reformed and broken to allow the immunoidentical spermatogonia to cross through the blood-testis barrier so they can become immunologically unique. Sertoli cells control the entry and exit of nutrients, hormones and other chemicals into the tubules of the testis as well as make the adluminal compartment an immune-privileged site.
...
Wikipedia
