Spermatids
| Spermatid | |
|---|---|
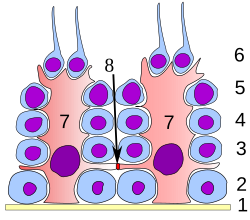
Germinal epithelium of the testicle.
1: basal lamina 2: spermatogonia 3: 1st order 4: spermatocyte 2nd order 5: spermatid 6: mature spermatid 7: Sertoli cell 8: tight junction (blood testis barrier) |
|

|
|
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | A05.360.490.890.860 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary . As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are connected by cytoplasmic material and have superfluous cytoplasmic material around their nuclei.
When formed, early round spermatids must undergo further maturational events to develop into spermatozoa, a process termed spermiogenesis (also termed spermeteliosis).
The spermatids begin to grow a living thread, develop a thickened mid-piece where the become localised, and form an acrosome. Spermatid DNA also undergoes packaging, becoming highly condensed. The DNA is packaged firstly with specific nuclear basic proteins, which are subsequently replaced with protamines during spermatid elongation. The resultant tightly packed chromatin is transcriptionally inactive.
In 2016 scientists at Nanjing Medical University claimed they had produced cells resembling mouse spermatids artificially from stem cells. They injected these spermatids into mouse eggs and produced pups.
Scheme showing analogies in the process of maturation of the ovum and the development of the Genyo spermatids (young spermatozoa).
...
Wikipedia
