Roman-era
| Roman Empire | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Capital |
Rome (27 BC – AD 410) Mediolanum (286–402, Western) |
|||||||||||
| Languages |
|
|||||||||||
| Religion |
|
|||||||||||
| Government | Mixed, functionally absolute monarchy | |||||||||||
| Emperor | ||||||||||||
| • | 27 BC – AD 14 | Augustus (first) | ||||||||||
| • | 98–117 | Trajan | ||||||||||
| • | 284–305 | Diocletian | ||||||||||
| • | 306–337 | Constantine I | ||||||||||
| • | 379–395 | Theodosius I | ||||||||||
| • | 474–480 | Julius Nepos | ||||||||||
| • | 527–565 | Justinian I | ||||||||||
| • | 976–1025 | Basil II | ||||||||||
| • | 1449–1453 | Constantine XI | ||||||||||
| Legislature | Senate | |||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical era to Late Middle Ages | |||||||||||
| • | Final War of the Roman Republic |
32–30 BC | ||||||||||
| • | Empire established | 30–2 BC | ||||||||||
| • |
Constantinople becomes capital |
330 | ||||||||||
| • | Final East West divide | 395 | ||||||||||
| • | Fall of the Western Roman Empire | 476 | ||||||||||
| • | Fourth Crusade | 1202–1204 | ||||||||||
| • | Reconquest of Constantinople | 1261 | ||||||||||
| • | Fall of Constantinople | 29 May 1453 | ||||||||||
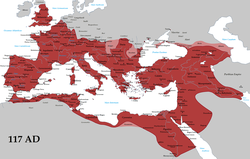
| Area | ||||||||||||
| • | 25 BC | 2,750,000 km² (1,061,781 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| • | AD 117 | 5,000,000 km² (1,930,511 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| • | AD 390 | 4,400,000 km² (1,698,849 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||
| • | 25 BC est. | 56,800,000 | ||||||||||
| Density | 20.7 /km² (53.5 /sq mi) | |||||||||||
| Currency | Sestertius,Aureus, Solidus, Nomisma | |||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
Mediolanum (286–402, Western)
Augusta Treverorum
Sirmium
Ravenna (402–476, Western)
Nicomedia (286–330, Eastern)
Constantinople (330–1453, Eastern)
Syracuse (663–669, Eastern)
The Roman Empire (Latin: Imperium Rōmānum; Classical Latin: [ɪmˈpɛ.ri.ũː roːˈmaː.nũː] Koine and Medieval Greek: Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, tr. Basileia tōn Rhōmaiōn) was the post-Roman Republic period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterized by government headed by emperors and large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. The city of Rome was the largest city in the world c. 100 BC – c. 400 AD, with Constantinople (New Rome) becoming the largest around 500 AD, and the Empire's populace grew to an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants (roughly 20% of the world's population at the time). The 500-year-old republic which preceded it was severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and political conflict, during which Julius Caesar was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44 BC. Civil wars and executions continued, culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesar's adopted son, over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the annexation of Egypt. Octavian's power was then unassailable and in 27 BC the Roman Senate formally granted him overarching power and the new title Augustus, effectively marking the end of the Roman Republic.
...
Wikipedia