Rio Conchos
| Río Conchos | |
|
Map of the Conchos
|
|
| Country | Mexico |
|---|---|
| State | Chihuahua (state) |
| Source | Sierra Madre Occidental |
| - location | Guadalupe, Chihuahua |
| Mouth | Rio Grande |
| - location | Ojinaga, Chihuahua |
| - coordinates | 29°35′N 104°25′W / 29.583°N 104.417°WCoordinates: 29°35′N 104°25′W / 29.583°N 104.417°W |
| Length | 560 km (348 mi) |
| Basin | 68,400 km2 (26,400 sq mi) |
| Discharge | for IBWC station 08-3730.00, near Ojinaga |
| - average | 24 m3/s (848 cu ft/s) |
| - max | 1,490 m3/s (52,619 cu ft/s) |
| - min | 0.09 m3/s (3 cu ft/s) |
|
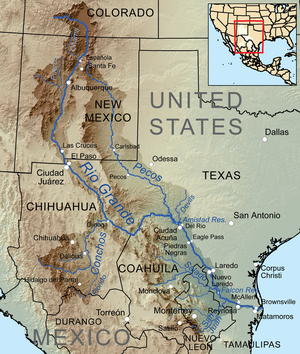
Map of the Rio Grande watershed, showing the Rio Conchos joining the Rio Grande near Ojinaga.
|
|
The Río Conchos (Conchos River) is a large river in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. It joins the Río Bravo del Norte (known in the United States as the Rio Grande) at the town of Ojinaga, Chihuahua.
The Rio Conchos is the main river in the state of Chihuahua and the Rio Grande's largest tributary. It is one of the most important river systems in all of northern Mexico. The Conchos has several reservoirs that make use of its water for agricultural and hydropower uses.
The Conchos rises in the Sierra Madre Occidental near Bocoyna in the municipality of Guadalupe, Chihuahua, where it heads east and receives several tributaries along the way. At Valle de Zaragoza municipality, Chihuahua, it is stopped at the La Boquilla Dam, the largest in Chihuahua forming Toronto Lake. It then heads east again, forming Colina Lake and then passes through Camargo, Chihuahua, the main agricultural center in the region, where it receives the Florido as a tributary.
From there, the Conchos heads north, receiving the San Pedro near Delicias, Chihuahua, entering the Chihuahua Desert and cutting a path through it, before turning to the northeast. At Aldama, Chihuahua, it is dammed by the Presa El Granero, then cuts through the Peguis Canyon, before forming a last dam (Toribio Ortega) near Ojinaga. At Ojinaga, it joins the Rio Bravo (Rio Grande in the U.S.).
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) has included the Rio Conchos in its Global 200 Freshwater Ecoregions assessment. The Global 200 is a list of freshwater ecoregions (rivers systems and lakes, for example) that the WWF considers of global importance for biodiversity conservation. The WWF's assessment of the Rio Conchos rates its biological distinctiveness as "globally outstanding" and its conservation status as critically endangered, putting it in the "priority I" category of needing conservation attention.
...
Wikipedia