Sierra Madre Occidental
| Sierra Madre Occidental | |
|---|---|

Río Grande de Santiago winding through the Sierra Madre Occidental, forming part of the border between Nayarit and Jalisco.
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Cerro Mohinora |
| Elevation | 10,863 ft (3,311 m) |
| Coordinates | 25°57′22″N 107°2′52″W / 25.95611°N 107.04778°WCoordinates: 25°57′22″N 107°2′52″W / 25.95611°N 107.04778°W |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 932 mi (1,500 km) NW x SE |
| Width | 150 mi (240 km) W x E |
| Geography | |
| Country | Mexico |
| State |
Sonora, Chihuahua, Sinaloa, Durango, Zacatecas, Nayarit, Jalisco, Aguascalientes, Guanajuato |
| Region | Northwestern Mexico |
| Borders on | |
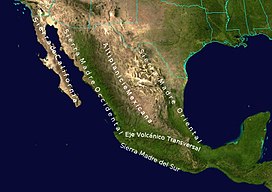
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through Northwestern and Western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica.
The Spanish name sierra madre means "mother mountains" and occidental means "western" in English, with these being the "Western Mother Mountains". To the east, from the Spanish oriental meaning "eastern" in English, the Sierra Madre Oriental range or "Eastern Mother Mountains" run generally parallel the Sierra Madre Occidental along eastern Mexico and the Gulf of Mexico.
The range extends from northern Sonora state near the Mexico-U.S. border at Arizona, southeastwards to the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt and Sierra Madre del Sur ranges. The high plateau that is formed by the range is cut by deep river valleys. This plateau is formed from volcanic rock overlying a basement of metamorphic rock.
This uplift has caused changes in weather patterns; increased rainfall occurring in the mountains has provided areas where ecosystems can form in wetter areas than surrounding land. This water-source forms watersheds that provide the arid surroundings with water that makes it possible to irrigate and farm crops. The wet ecosystems are islands of biodiversity, differing significantly from what would otherwise be a desert landscape. Oak forests are the predominant plant life and extend into the low land deserts.
...
Wikipedia