RB-101
 |
|
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
|
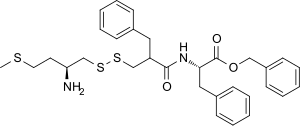
| Synonyms | RB-101; phenylmethyl (2S)-2-[(2-([(2S)-2-amino-4-methylsulfanylbutyl]disulfanylmethyl)-3-phenylpropanoyl)amino]-3-phenylpropanoate |
| CAS Number |
135949-60-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 119600 |
| ChemSpider | 106792 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C31H38N2O3S3 |
| Molar mass | 582.84 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
RB-101 is a drug that acts as an enkephalinase inhibitor, which is used in scientific research.
RB-101 is a prodrug which acts by splitting at the disulfide bond once inside the brain, to form two selective enzyme inhibitors and blocking both types of the zinc-metallopeptidase enkephalinase enzymes. This inhibits the breakdown of the endogenous opioid peptides known as enkephalins. These two enzymes, aminopeptidase N (APN) and neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (NEP), are responsible for the breakdown of both kinds of enkephalin naturally found in the body, and so RB-101 causes a buildup of both Met-enkephalin and Leu-enkephalin.
These peptides act primarily at the delta opioid receptor, although they also stimulate the mu opioid receptor to some extent through a delta-opioid receptor mediated interaction with another peptide cholecystokinin, and the enzyme-inhibiting effects of RB-101 thus produce indirect stimulation of both of these opioid receptor subtypes. This causes RB-101 to be strongly synergistic with cholecystokinin antagonists.
Unlike the more commonly used enkephalinase inhibitor racecadotril, which only acts peripherally and has antidiarrheal effects, RB-101 is able to enter the brain, and thus produces a range of effects, acting as an analgesic, anxiolytic and antidepressant. The antidepressant and anxiolytic actions are thought to be mediated through the delta opioid receptor, while the analgesic effects most likely result from a mix of mu and delta activity. Animal studies suggest that RB-101 is also likely to be useful in relieving the symptoms of acute opioid withdrawal and in the management of opioid dependence.
...
Wikipedia
