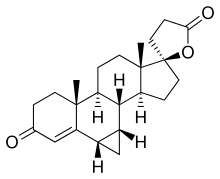
Prorenone
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | SC-23133; 3-(17β-Hydroxy-6β,7β-methylene-3-oxo-4-androsten-17α-yl)propionic acid γ-lactone |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H30O3 |
| Molar mass | 354.48 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Prorenone (developmental code name SC-23133) is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group related to spironolactone that was never marketed. It is the lactonic form of prorenoic acid (prorenoate), and prorenoate potassium (SC-23992), the potassium salt of prorenoic acid, also exists. Prorenoate potassium is about 8 times more potent than spironolactone as an antimineralocorticoid in animals, and it may act as a prodrug to prorenone. In addition to the mineralocorticoid receptor, prorenone also binds to the glucocorticoid, androgen, and progesterone receptors. Similarly to spironolactone, prorenone is also a potent inhibitor of aldosterone biosynthesis.
Prorenone can be synthesized via a Johnson–Corey–Chaykovsky reaction by reaction of canrenone with trimethylsulfonium iodide and sodium hydride.
...
Wikipedia
