Polyglycolide
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
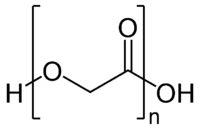
Poly[oxy(1-oxo-1,2-ethanediyl)]
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
26009-03-0 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
| Properties | |
| (C2H2O2)n | |
| Molar mass | (58.04)n |
| Density | 1.530 g/cm3 at 25 °C |
| Melting point | 225 to 230 °C (437 to 446 °F; 498 to 503 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Polyglycolide or poly(glycolic acid) (PGA), also spelled as polyglycolic acid, is a biodegradable, thermoplastic polymer and the simplest linear, aliphatic polyester. It can be prepared starting from glycolic acid by means of polycondensation or ring-opening polymerization. PGA has been known since 1954 as a tough fiber-forming polymer. Owing to its hydrolytic instability, however, its use has initially been limited. Currently polyglycolide and its copolymers (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) with lactic acid, poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) with ε-caprolactone, and poly (glycolide-co-trimethylene carbonate) with trimethylene carbonate) are widely used as a material for the synthesis of absorbable sutures and are being evaluated in the biomedical field.
Polyglycolide has a glass transition temperature between 35 and 40 °C and its melting point is reported to be in the range of 225-230 °C. PGA also exhibits an elevated degree of crystallinity, around 45-55%, thus resulting in insolubility in water. The solubility of this polyester is somewhat unusual, in that its high molecular weight form is insoluble in almost all common organic solvents (acetone, dichloromethane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, tetrahydrofuran), while low molecular weight oligomers sufficiently differ in their physical properties to be more soluble. However, polyglycolide is soluble in highly fluorinated solvents like hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) and hexafluoroacetone sesquihydrate, that can be used to prepare solutions of the high MW polymer for melt spinning and film preparation. Fibers of PGA exhibit high strength and modulus (7 GPa) and are particularly stiff.
...
Wikipedia
