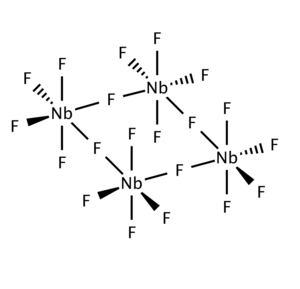
Niobium(V) fluoride
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC names
Niobium(V) fluoride
Niobium pentafluoride |
|
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.109 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| Properties | |
| NbF5 | |
| Molar mass | 187.898 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless monoclinic crystals hygroscopic |
| Density | 3.293 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 72 to 73 °C (162 to 163 °F; 345 to 346 K) |
| Boiling point | 236 °C (457 °F; 509 K) |
| reacts | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in chloroform, carbon disulfide, sulfuric acid |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions
|
Niobium(V) chloride Niobium(V) bromide Niobium(V) iodide |
|
Other cations
|
Vanadium(V) fluoride Tantalum(V) fluoride |
|
Related niobium fluorides
|
Niobium(III) fluoride Niobium(IV) fluoride |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Niobium(V) fluoride, also known as niobium pentafluoride, is a colorless crystalline solid often used as a starting material in niobium chemistry.
Niobium pentafluoride is obtained as an intermediate during the recovery of niobium metal from its ores. It also can be prepared by direct fluorination of niobium metal at 250 to 300 °C, either by fluorine gas or anhydrous hydrofluoric acid. The pentafluoride vapors are condensed in a pyrex or quartz tube from which it is sublimed at 120 °C under vacuum and collected as colorless crystals.
Also, niobium pentafluoride can be prepared by the reaction of fluorine with niobium pentachloride:
...
Wikipedia
