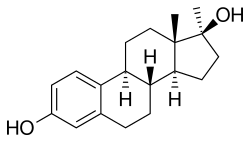
Methylestradiol
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, Renodiol |
| Synonyms | 17α-Methylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol; NSC-52245 |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 286.40854 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Methylestradiol, or 17α-methylestradiol (17α-ME), is a semisynthetic, steroidal estrogen that has been sold in combination with normethandrone (methylestrenolone), an anabolic-androgenic steroid and progestin and , under brand names including Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, Renodiol for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in Brazil, Venezuela, and Indonesia. Due to the presence of the 17α-methyl group, methylestradiol cannot be deactivated by oxidation of the 17β-hydroxy group, resulting in improved metabolic stability and potency relative to estradiol analogously to ethinylestradiol (17α-ethynylestradiol). In addition to its clinical use, methylestradiol has been studied as a radiopharmaceutical.
Methylestradiol is an active metabolite of the anabolic-androgenic steroids methyltestosterone (17α-methyltestosterone) and metandienone (17α-methyl-δ1-testosterone) and is responsible for their estrogenic side effects such as gynecomastia (breast development) and fluid retention.
...
Wikipedia
