Maltose
 α-Maltose
|
|
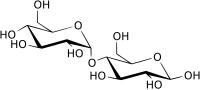 β-Maltose
|
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[4,5,6-trihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxyox ane-3,4,5-triol
|
|
| Other names
4-O-α-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucose
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
69-79-4 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:17306 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL1234209 |
| ChemSpider |
388329 α-maltose 6019 β-maltose |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.651 |
| EC Number | 200-716-5 |
| PubChem | 6255 |
| UNII |
66Y63L379N |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.30 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder or crystals |
| Density | 1.54 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 160 to 165 °C (320 to 329 °F; 433 to 438 K) (anhydrous) 102–103 °C (monohydrate) |
| 1.080 g/mL (20 °C) | |
|
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+140.7° (H2O, c = 10) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related
|
Sucrose Lactose Trehalose Cellobiose |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Maltose (/ˈmɔːltoʊs/ or /ˈmɔːltoʊz/), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond, formed from a condensation reaction. The isomer isomaltose has two glucose molecules linked through an α(1→6) bond.
Maltose is the second member of an important biochemical series of glucose chains. Maltose is the disaccharide produced when amylase breaks down starch. It is found in germinating seeds as they break down their starch stores to use for food, which is why it was named after malt. It is also produced when glucose is caramelized.
Maltose was discovered by Irish chemist and brewer Cornelius O'Sullivan in 1872. Its name comes from malt, from Old English mealt, of Germanic origin, and the suffix '–ose', a suffix denoting names of sugars and other carbohydrates.
Maltose is a biomolecule that belongs to the group of carbohydrates within the division of biomolecules into the three main groups: carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen C, O, H and are either polyhydroxyaldehydes or polyhydroxyketones.
...
Wikipedia
