Cellobiose
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
528-50-7 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:17057 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL1614877 |
| ChemSpider |
388323 |
| DrugBank |
DB02061 |
| KEGG |
C00185 |
| PubChem |
294 439178 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.30 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white, hard powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.768 g/mL |
| Melting point | 203.5 °C (398.3 °F; 476.6 K) (decomposes) |
| 12 g/100mL | |
| Solubility | very slightly soluble in alcohol insoluble in ether, chloroform |
| log P | -5.03 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.39 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma-Aldrich |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
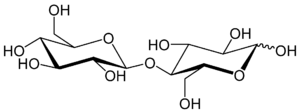
Cellobiose is a disaccharide with the formula [HOCH2CHO(CHOH)3]2O. Cellobiose, a reducing sugar, consists of two β-glucose molecules linked by a β(1→4) bond. It can be hydrolyzed to glucose enzymatically or with acid. Cellobiose has eight free alcohol (OH) groups, one acetal linkage and one hemiacetal linkage, which give rise to strong inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonds. It can be obtained by enzymatic or acidic hydrolysis of cellulose and cellulose rich materials such as cotton, jute, or paper.
Treatment of cellulose with acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid, gives cellobiose octoacetate, which is no longer a hydrogen bond donor (though it is still a hydrogen bond acceptor) and is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents.
...
Wikipedia

