Cellulose
 |
|
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
9004-34-6 |
|
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL2109009 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.692 |
| EC Number | 232-674-9 |
| E number | E460 (thickeners, ...) |
| UNII |
SMD1X3XO9M |
| Properties | |
| (C 6H 10O 5) n |
|
| Appearance | white powder |
| Density | 1.5 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 260–270 °C; 500–518 °F; 533–543 K decomposes |
| none | |
| Thermochemistry | |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−963,000 J/mol |
|
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH |
−2828,000 J/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 15 mg/m3 (total) TWA 5 mg/m3 (resp) |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 mg/m3 (total) TWA 5 mg/m3 (resp) |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D. |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Starch |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
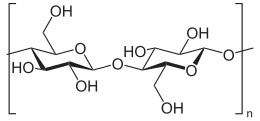
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C
6H
10O
5)
n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50% and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%.
Cellulose is mainly used to produce paperboard and paper. Smaller quantities are converted into a wide variety of derivative products such as cellophane and rayon. Conversion of cellulose from energy crops into biofuels such as cellulosic ethanol is under investigation as an alternative fuel source. Cellulose for industrial use is mainly obtained from wood pulp and cotton.
...
Wikipedia

