Madurai nayak
| Madurai Nayak dynasty | |||||
|
|||||
|
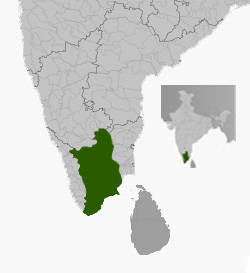
Approximate extent of the Madurai Nayak Kingdom, circa 1570.
|
|||||
| Capital |
Madurai (1529–1616) Tiruchirapalli |
||||
| Languages | Telugu, Tamil | ||||
| Government | Governors, then Monarchy | ||||
| History | |||||
| • | Established | 1529 | |||
| • | Disestablished | 1736 | |||
| Preceding States | Succeeding States
|
Breakaway States
|
| Kings and Queen Regents of Madurai Nayak Dynasty |
|
|---|---|
| Part of History of Tamil Nadu | |
 |
|
| Madurai Nayak rulers | |
| Viswanatha Nayak | 1529–1563 |
| Kumara Krishnappa Nayak | 1563–1573 |
| Joint Rulers Group I | 1573–1595 |
| Joint Rulers Group II | 1595–1602 |
| Muttu Krishnappa Nayak | 1602–1609 |
| Muttu Virappa Nayak | 1609–1623 |
| Tirumalai Nayak | 1623–1659 |
| Muthu Alakadri Nayak | 1659–1662 |
| Chokkanatha Nayak | 1662–1682 |
| Rangakrishna Muthu Virappa Nayak | 1682–1689 |
| Rani Mangammal‡ | 1689–1704 |
| Vijaya Ranga Chokkanatha Nayak | 1704–1731 |
| Queen Meenakshi‡ | 1731–1736 |
| ‡ Regent Queens | |
| Capitals | |
| Madurai | 1529–1616 |
| Tiruchirapalli | 1616–1634 |
| Madurai | 1634–1665 |
| Tiruchirapalli | 1665–1736 |
| Major forts | |
| Madurai 72 Bastion Fort | |
| Tiruchirapalli Rock Fort | |
| Dindigul Fort | |
| Thirunelvelli Fort | |
| other Military forts | |
| Namakkal Fort | |
| Sankagiri Fort | |
| Attur Fort | |
| Palaces | |
| Thirumalai Nayak Mahal, Madurai | |
| Chokkanatha Nayak Palace a.k.a. Durbar Hall, Tiruchirapalli | |
| Rani Mangammal Tamukkam palace Madurai | |
Tiruchirapalli
(1616–1634)
Madurai
(1634–1695)
Tiruchirapalli
(1695-1716)
Madurai
(1716–1736)
The Madurai Nayaks were rulers from around 1529 until 1736, of a region comprising most of modern-day Tamil Nadu, India, with Madurai as their capital. The Nayak reign was an era noted for its achievement in arts, cultural and administrative reforms, revitalization of temples previously ransacked by the Delhi Sultans, and inauguration of a unique architectural style.
The dynasty consisted of 13 rulers, of whom 9 were kings, 2 were queens, and 2 were joint-kings. The most notable of these were the king, Thirumalai Naicker, and the queen, Rani Mangammal. Foreign trade was conducted mainly with the Dutch and the Portuguese, as the British and the French had not yet made inroads in the region.
Madurai Nayaks belonged to the Balija social group.
Early in the 14th century, a dispute arose over the succession to the Pandya throne. One claimant appealed for help to emperor Ala-ud-din of Delhi, who dispatched his general, Malik Kafur, in 1310. Malik Kafur marched south, ransacking kingdoms on the way and causing enormous changes to the political configuration of central and Southern India. He marched into Madurai, sacking the town, paralysing trade, suppressing public worship, and making civilian life miserable. The great Meenakshi temple with its fourteen towers was pulled down, destroying the nearby streets and buildings, and leaving only the two shrines of Sundaresvara and Meenakshi intact. The events are controversial: as another account describes them,
...the Deccan was soon to feel the force of Islam, which was already the master of Northern India. In the reign of the able sultan of Delhi, Ala-ud-din Khalji (1296—1315 AD), a series of brilliant raids, led by the eunuch general Malik Kafur, a converted Hindu, crushed the Deccan kingdoms, and for a time a sultanate was set up even in Madurai, in the extreme south.
...
Wikipedia