Lead(II) fluoride
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Lead difluoride
plumbous fluoride |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
7783-46-2 |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.089 |
| PubChem | 24549 |
| Properties | |
| PbF2 | |
| Molar mass | 245.20 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 8.445 g/cm3 (orthorhombic) 7.750 g/cm3 (cubic) |
| Melting point | 824 °C (1,515 °F; 1,097 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,293 °C (2,359 °F; 1,566 K) |
| 0.057 g/100 mL (0 °C) 0.0671 g/100 mL (20 °C) |
|
|
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
2.05 x 10−8 (20 °C) |
| Solubility | soluble in nitric acid; insoluble in acetone and ammonia |
| −-58.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
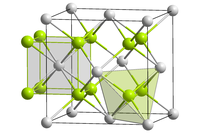
| Structure | |
| Fluorite (cubic), cF12 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
3031 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions
|
Lead(II) chloride Lead(II) bromide Lead(II) iodide |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Lead(II) fluoride (PbF2) is a chemical compound that is an odorless white solid.
Conditions/substances to avoid are: strong oxidizers.
Lead(II) fluoride is used:
Lead(II) fluoride can be prepared by several methods. It is obtained by treating lead(II) hydroxide or lead(II) carbonate with hydrofluoric acid, followed by evaporation of the solution:
Alternatively, it is precipitated by adding hydrofluoric acid to a lead(II) salt solution, or by adding potassium fluoride to a lead(II) nitrate solution.
...
Wikipedia
