Ku (protein)
Ku is a dimeric protein complex that binds to DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. Ku is evolutionarily conserved from bacteria to humans. The ancestral bacterial Ku is a homodimer (two copies of the same protein bound to each other). Eukaryotic Ku is a heterodimer of two polypeptides, Ku70 (XRCC6) and Ku80 (XRCC5), so named because the molecular weight of the human Ku proteins is around 70 kDa and 80 kDa. The two Ku subunits form a basket-shaped structure that threads onto the DNA end. Once bound, Ku can slide down the DNA strand, allowing more Ku molecules to thread onto the end. In higher eukaryotes, Ku forms a complex with the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) to form the full DNA-dependent protein kinase, DNA-PK. Ku is thought to function as a molecular scaffold to which other proteins involved in NHEJ can bind, orienting the double-strand break for ligation.
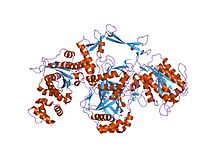
The Ku70 and Ku80 proteins consist of three structural domains. The N-terminal domain is an alpha/beta domain. This domain only makes a small contribution to the dimer interface. The domain comprises a six stranded beta sheet of the Rossman fold. The central domain of Ku70 and Ku80 is a DNA-binding beta-barrel domain. Ku makes only a few contacts with the sugar-phosphate backbone, and none with the DNA bases, but it fits sterically to major and minor groove contours forming a ring that encircles duplex DNA, cradling two full turns of the DNA molecule. By forming a bridge between the broken DNA ends, Ku acts to structurally support and align the DNA ends, to protect them from degradation, and to prevent promiscuous binding to unbroken DNA. Ku effectively aligns the DNA, while still allowing access of polymerases, nucleases and ligases to the broken DNA ends to promote end joining. The C-terminal arm is an alpha helical region which embraces the central beta-barrel domain of the opposite subunit. In some cases a fourth domain is present at the C-terminus, which binds to DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit.
...
Wikipedia