Januvia
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a606023 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 87% |
| Protein binding | 38% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4- and CYP2C8-mediated) |
| Biological half-life | 8 to 14 h |
| Excretion | Renal (80%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.217.948 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
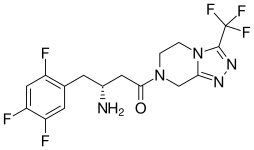
| Formula | C16H15F6N5O |
| Molar mass | 407.314 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Sitagliptin (INN; ![]() i/sɪtəˈɡlɪptɪn/, previously identified as MK-0431 and marketed as the phosphate salt under the trade name Januvia) is an oral antihyperglycemic (antidiabetic drug) of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class. It was developed, and is marketed, by Merck & Co. This enzyme-inhibiting drug is used either alone or in combination with other oral antihyperglycemic agents (such as metformin or a thiazolidinedione) for treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2.
i/sɪtəˈɡlɪptɪn/, previously identified as MK-0431 and marketed as the phosphate salt under the trade name Januvia) is an oral antihyperglycemic (antidiabetic drug) of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class. It was developed, and is marketed, by Merck & Co. This enzyme-inhibiting drug is used either alone or in combination with other oral antihyperglycemic agents (such as metformin or a thiazolidinedione) for treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2.
Side effects are as common with sitagliptin (whether used alone or with metformin or pioglitazone) as they were with placebo, except for rare nausea and common cold-like symptoms, including photosensitivity. There is no significant difference in the occurrence of hypoglycemia between placebo and sitagliptin. In those taking sulphonylureas there is an increased risk of low blood sugar.
...
Wikipedia
