Interleukin 12
| Human Interleukin 12 | |
|---|---|
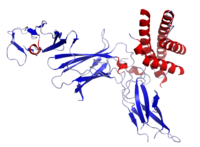
Crystal structure of human IL-12
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | IL12, p70 |
| PDB | 1F45 |
| IL12A | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | IL12A |
| Alt. symbols | CLMF1, NKSF1, p35 |
| Entrez | 3592 |
| HUGO | 5969 |
| OMIM | 161560 |
| RefSeq | NM_000882 |
| UniProt | P29459 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 3 p12-q13.2 |
| interleukin 12B | |
|---|---|
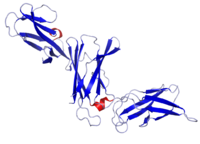
Crystal structure of IL-12B
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | IL12B |
| Alt. symbols | CLMF2, NKSF2, p40 |
| Entrez | 3593 |
| HUGO | 5970 |
| OMIM | 161561 |
| PDB | 1F42 |
| RefSeq | NM_002187 |
| UniProt | P29460 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 5 q31.1-33.1 |
Interleukin 12 (IL-12) is an interleukin that is naturally produced by dendritic cells,macrophages, neutrophils, and human B-lymphoblastoid cells (NC-37) in response to antigenic stimulation.
IL-12 is composed of a bundle of four alpha helices. It is a heterodimeric cytokine encoded by two separate genes, IL-12A (p35) and IL-12B (p40). The active heterodimer (referred to as 'p70'), and a homodimer of p40 are formed following protein synthesis.
IL-12 is involved in the differentiation of naive T cells into Th1 cells. It is known as a T cell-stimulating factor, which can stimulate the growth and function of T cells. It stimulates the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) from T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, and reduces IL-4 mediated suppression of IFN-γ. T cells that produce IL-12 have a coreceptor, CD30, which is associated with IL-12 activity.
IL-12 plays an important role in the activities of natural killer cells and T lymphocytes. IL-12 mediates enhancement of the cytotoxic activity of NK cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. There also seems to be a link between IL-2 and the signal transduction of IL-12 in NK cells. IL-2 stimulates the expression of two IL-12 receptors, IL-12R-β1 and IL-12R-β2, maintaining the expression of a critical protein involved in IL-12 signaling in NK cells. Enhanced functional response is demonstrated by IFN-γ production and killing of target cells.
...
Wikipedia
