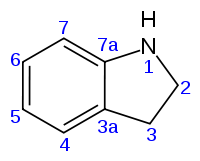
Indoline
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
2,3-dihydro-1H-indole
|
|
| Other names
2,3-Dihydroindole
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| 111915 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.107 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | NL6906300 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C8H9N | |
| Molar mass | 119.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.063 g/mL |
| Melting point | −21 °C (−6 °F; 252 K) |
| Boiling point | 220 to 221 °C (428 to 430 °F; 493 to 494 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Fisher Scientific |
| Flash point | 92.8 °C (199.0 °F; 365.9 K) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related aromatics
|
carbazole, indole, isoindoline, oxindole |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Indoline is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C8H9N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound is based on the indole structure, but the 2-3 bond is saturated. By oxidation/dehydrogenation it can be converted to indoles.
Indoline was used to make Indocaine.
...
Wikipedia
