Idelalisib
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation |
/aɪˈdɛləlɪˌsɪb/ eye-DEL-ə-li-sib |
| Trade names | Zydelig |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | zydelig |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >84% |
| Metabolism | Aldehyde oxidase (~70%), CYP3A4 (~30%);UGT1A4 (minor) |
| Metabolites | GS-563117 (inactive in vitro) |
| Onset of action | Tmax = 1.5 hours |
| Biological half-life | 8.2 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (78%), urine (14%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | GS-1101, CAL-101 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.235.089 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
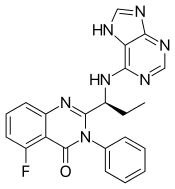
| Formula | C22H18FN7O |
| Molar mass | 415.42 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Idelalisib (trade name Zydelig zye-DEL-ig, codenamed GS-1101 or CAL-101) is a drug used for the treatment of certain hematological malignancies. The substance acts as a phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor; more specifically, it blocks P110δ, the delta isoform of the enzyme phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
Idelalisib is a second-line drug for patients whose chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has relapsed. Used in combination with rituximab, idelalisib is to be used in patients for whom rituximab alone would be considered appropriate therapy due to other existing medical conditions. It appears to be very effective and leads to rapid resolution of lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. However, the lymphocyte counts takes longer to decrease to normal levels with idelalisib. Idelalisib is effective in patients who have a p53 mutation, which otherwise tends to impart a poor prognosis in CLL patients. This is important as even the first line chemotherapy regimens, such as those incorporating fludarabine are ineffective in patients with p53 mutation.
It is also approved for the treatment of follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (FL) and relapsed small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), both in patients who have received at least two prior systemic therapies.
It was also being studied in clinical trials for first-line treatment in high-risk CLL patients, who are otherwise unable to tolerate aggressive chemotherapy due to their medical history or age, but these trials were terminated due to adverse effects.
Clinical symptoms include diarrhea, fever, fatigue, nausea, cough, pneumonia, abdominal pain, chills and rash. Laboratory abnormalities may include: neutropenia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglycemia and elevated levels of liver enzymes. Idelalisib's safety and effectiveness to treat relapsed FL and relapsed SLL were established in a clinical trial with 123 participants with slow-growing (indolent) non-Hodgkin lymphomas. All participants were treated with idelalisib and were evaluated for complete or partial disappearance of their cancer after treatment (objective response rate, or ORR). Results showed 54% of participants with relapsed FL and 58% of participants with SLL experienced ORR.
...
Wikipedia
