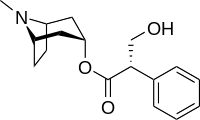
Hyoscyamine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Anaspaz, Levbid, Levsin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a684010 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral, Injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% Protein binding |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 3–5 hrs. |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.667 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 289.375 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hyoscyamine (also known as daturine) is a tropane alkaloid. It is a secondary metabolite found in certain plants of the family Solanaceae, including henbane (Hyoscyamus niger), mandrake (Mandragora officinarum), jimsonweed (Datura stramonium), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna). It is the levorotary isomer of atropine (third of the three major nightshade alkaloids) and thus sometimes known as levo-atropine. Hyoscyamine should not be confused with hyoscine, an older alternate name for the related nightshade-derived anticholinergic scopolamine for which it is the precursor.
Brand names for hyoscyamine include Symax, HyoMax, Anaspaz, Egazil, Buwecon, Cystospaz, Levsin, Levbid, Levsinex, Donnamar, NuLev, Spacol T/S and Neoquess.
Hyoscyamine is an antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (antimuscarinic). It blocks the action of acetylcholine at parasympathetic sites in sweat glands, salivary glands, stomach secretions, heart muscle, sinoatrial node, smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal tract, and the central nervous system. It increases cardiac output and heart rate, lowers blood pressure and dries secretions. It may antagonize serotonin. At comparable doses, hyoscyamine has 98 per cent of the anticholinergic power of atropine. The other major belladonna-derived drug scopolamine has 92 per cent of the antimuscarinic potency of atropine.
...
Wikipedia
